Medical / Pain Relief
Plantar Fasciitis
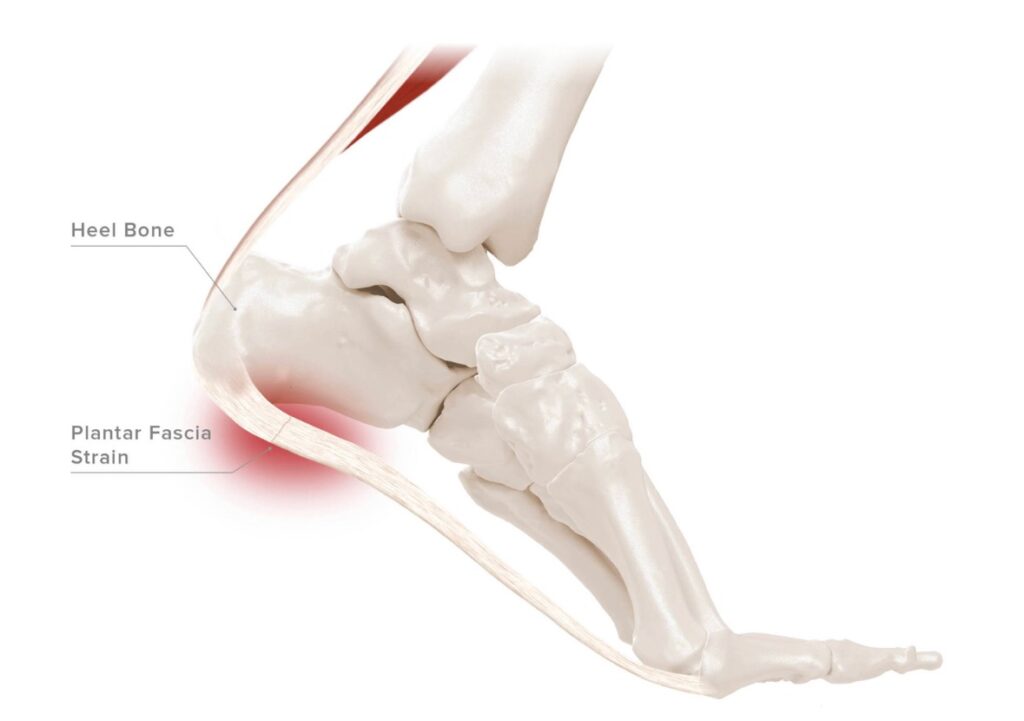
Plantar fasciitis is a common overuse injury felt at the bottom of the heel. Plantar fasciitis occurs when the plantar aponeurosis or the plantar fascia which supports the arch of the foot becomes irritated and inflamed.
It’s common for patients with plantar fasciitis to also have heel spurs. Issues involving the plantar fascia usually revolve around poor biomechanics.
Pronation / Supination
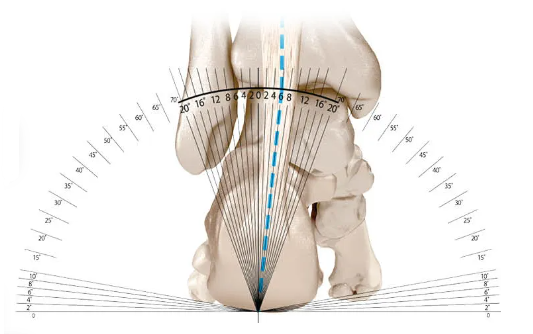
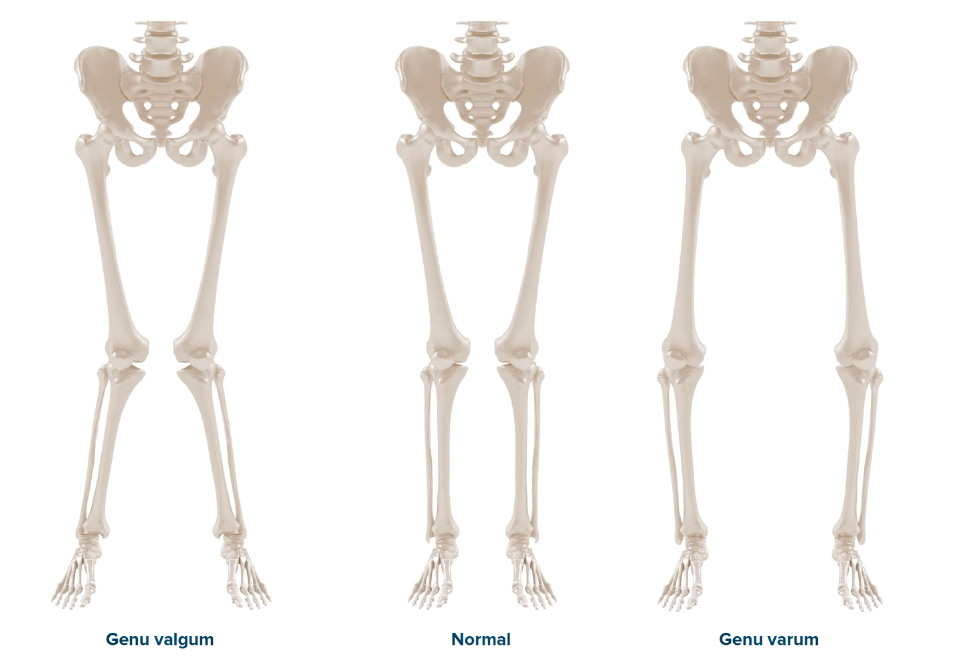
Your foot rolls inwards it is called pronation, it is a naturally occurring and normal motion in the foot which involves your foot rolling inwards. When the foot over pronates there is an issue as it places excessive stresses on soft tissue of the foot leg and ankle. Excessive pronation can lead to complaints such as shin splints, plantar fasciitis, posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, knee pain, hip pain and even lower back pain.
When your foot rolls outwards it is called supination. Supination is the opposite of pronation; it is where the foot rolls outwards so that the lateral edge of the foot is mostly in contact with the ground, the foot may also have an extremely high arch. Those who excessively supinate may find their outer ankle and leg become painful as well as their arch.
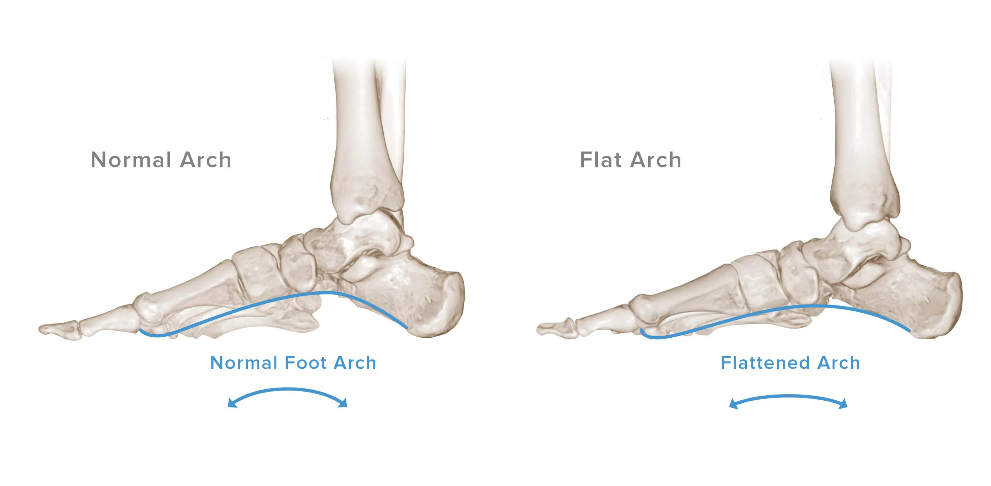
Flat Feet
There are two major forms of flatfoot:
Adult Acquired Flatfoot: This cause of flatfoot is due to the dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon. Go to that section of the pathology section to review this form of flatfoot.
Flexible Flatfoot: This form of flatfoot originates in childhood due to the skipped development of the medial longitudinal arch past the age of 5. This condition is known to usually be bilateral and have the arch of the foot return to normal when not in weight-bearing. It’s possible that 20% of adults have flexible flatfoot, but that the condition goes unrecognized due to being asymptomatic.
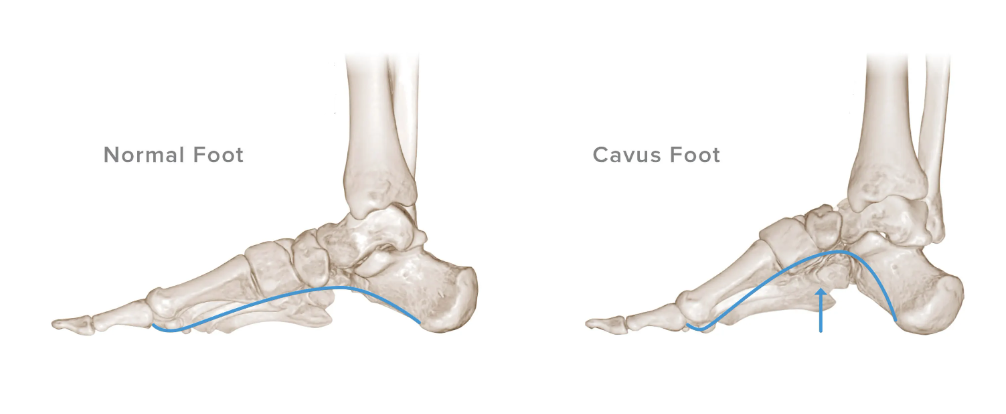
High Arch
Pes cavus, a high-arched foot or cavus foot is a condition in which the foot has a very high arch. Due to the increased arch, the pressure and force applied on the heel and ball of the foot are increased during physical activity. Cavus foot is either the result of a congenital condition or, usually, a progressive neuropathic disorder.
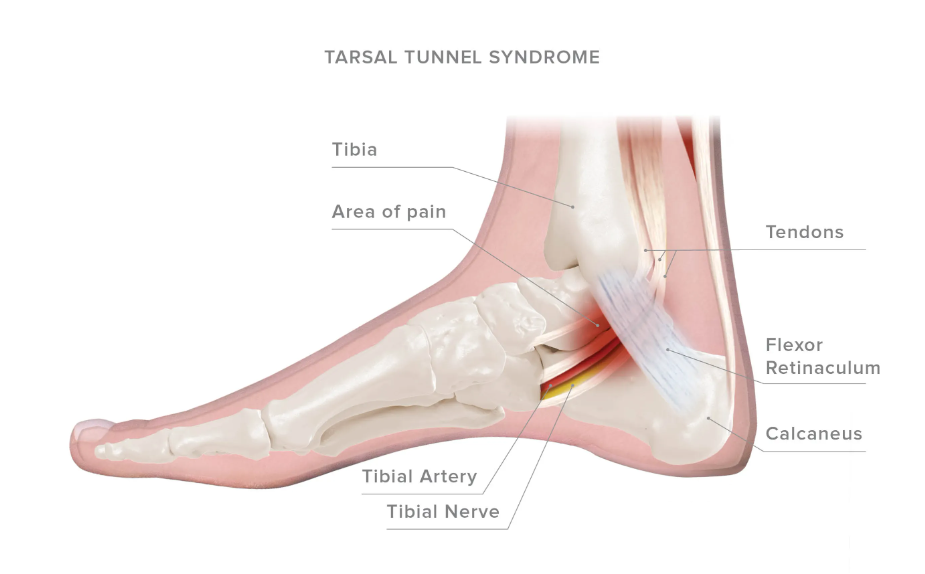
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
The tarsal tunnel is a space inside the outer aspect of the ankle near the bones. Arteries, veins, tendons and nerves run through this tunnel, compression or squeezing of this tunnel can cause the nerve to be pinched.
Compression of the tunnel can be due to repetitive wear, flat feet, anomalous structures, injuries, arthritis, diabetes and other conditions. If untreated, the condition can be progressive and will continue to get worse.
Knee Pain
A torn meniscus is a common knee injury that occurs due to forceful twisting or rotation of the knee, while it is fully weight bearing.
Know as inflammation of a bursa (fluid cushion between bone and soft tissue) located near your knee joint.
A common cause of knee pain in growing adolescents. It is an inflammation of the area just below the knee where the tendon from the kneecap (patellar tendon) attaches to the shinbone (tibia).
is the most common cause of knee pain and is caused by imbalances in the forces controlling the way the knee cap (patella) moves during knee flexion (tensing) and extension (straightening).
an injury to the tendon connecting your kneecap (patella) to your shinbone. The patellar tendon works with the muscles at the front of your thigh to straighten your knee so you can kick, run and jump
There are four main ligaments in the knee that can become injured. During injury, a knee ligament may be stretched (sprained), or torn (ruptured).
is the most common form of arthritis in the knee.
It is a degenerative, “wear-and-tear” type of arthritis that occurs most often in people 50 years of age and older, but sometimes may occur in younger people as well.
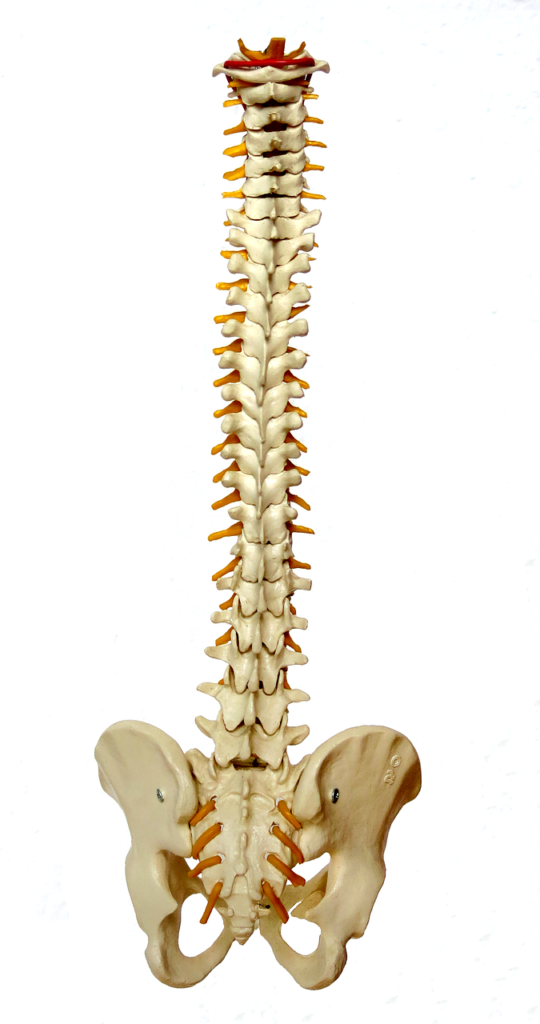
Back Pain
There are many causes of lower back pain. These include structural misalignment, hereditary disorders, disc degeneration in the spine, nerve damage, muscle imbalance and dysfunction of the lower back/pelvic region caused by poor timing or function of the feet and legs when walking.
Very often it is a combination of a number of these factors and that’s why if only one area is treated the condition improves but does not completely resolve.
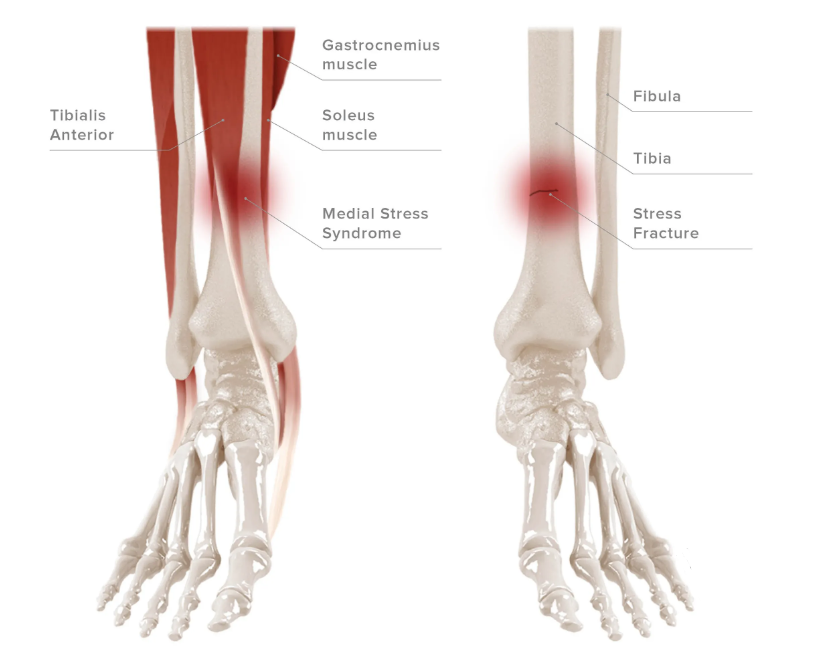
Shin Splints
Shin splints is a broad term used to describe pain and swelling in the outer aspect of the tibia or shins.
Shin splints are usually the result of repetitive stress on the bone due to excessive physical activity with little rest and poor biomechanics. Untreated and unresolved, shin splints can result in stress fractures.
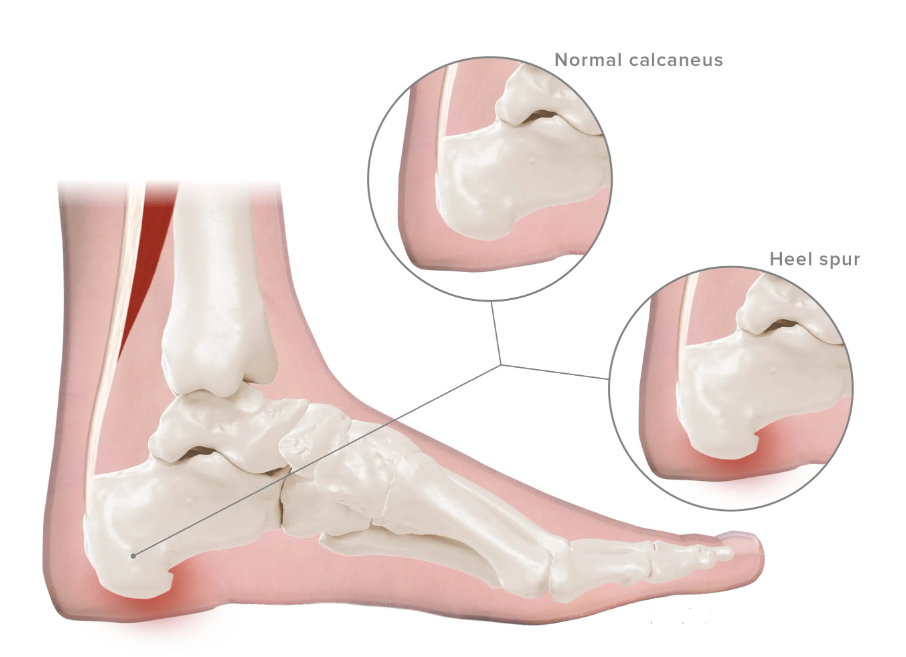
Heel / Bone Spurs
The foot handles a lot of forces during walking and physical activity. Some of the highest forces in the foot are at the heel due to impact with the ground.
A lot of repetitive stress can wear down the tissues in the foot and cause heel problems.
Heel pain will usually heal on its own, but if the repetitive stress is unchecked, the condition can become problematic and chronic.
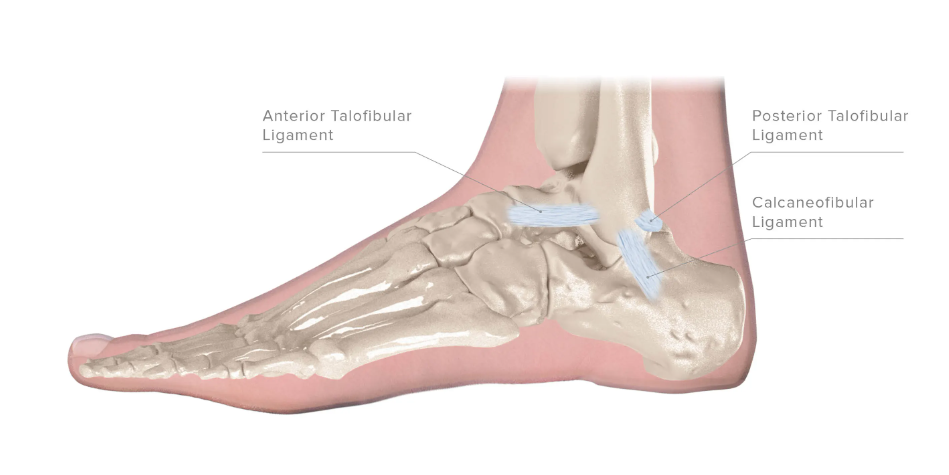
Ankle Sprain / Ankle Instability
Ankle sprains occur when the ligaments that support and stabilize the area are injured due to excess stretching and possible tearing. Patients may report this injury having occurred as a twisting of their ankle.
Severe strains can make it likely for recurrent ankle strains and pains in the future. The majority of ankle sprains occur in the lateral or outward facing ligaments of the ankle. The degree of severity of an ankle sprain depends on the degree of tearing that occurs in that ligament
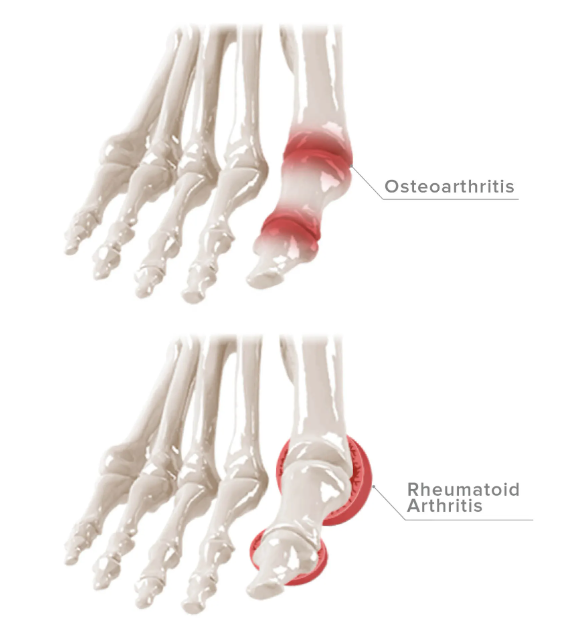
Ankle & Foot Arthritis
Arthritis is a broad description term used to categorize conditions consisting of dysfunctions of the joints. Close to 50% of the elderly in their 60s and 70s have arthritis of the foot and ankle, but not all are symptomatic.
The most common type of arthritis is osteoarthritis. Another type, but less common is rheumatoid arthritis.
Patients that have had broken bones, torn ligaments and sprains are more likely to develop arthritis in those past affected areas.
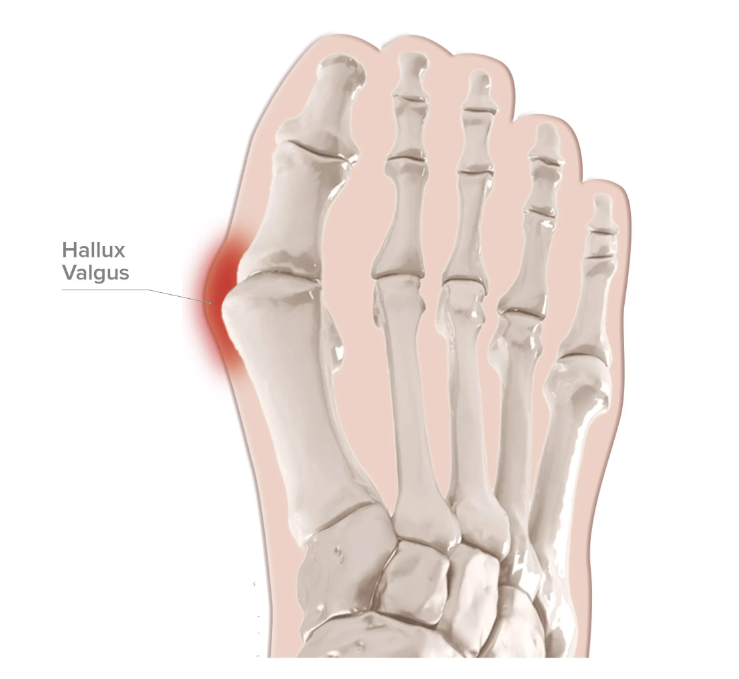
Hallux Valgus / Bunions
Hallux valgus or bunions occur at the joint that connects the big toe to the foot, also known as the metatarsophalangeal joint. Visibly, bunions appear like a bump on the base and side of the big toe. In actuality, the big toe begins to angle inward toward the second toe, placing it and the joint out of alignment.
One in three women in the U.S. have bunions, and 9 out of 10 cases of bunions occur in women. Bunions are a progressive disorder and worsen with time.
Diabetic Care:
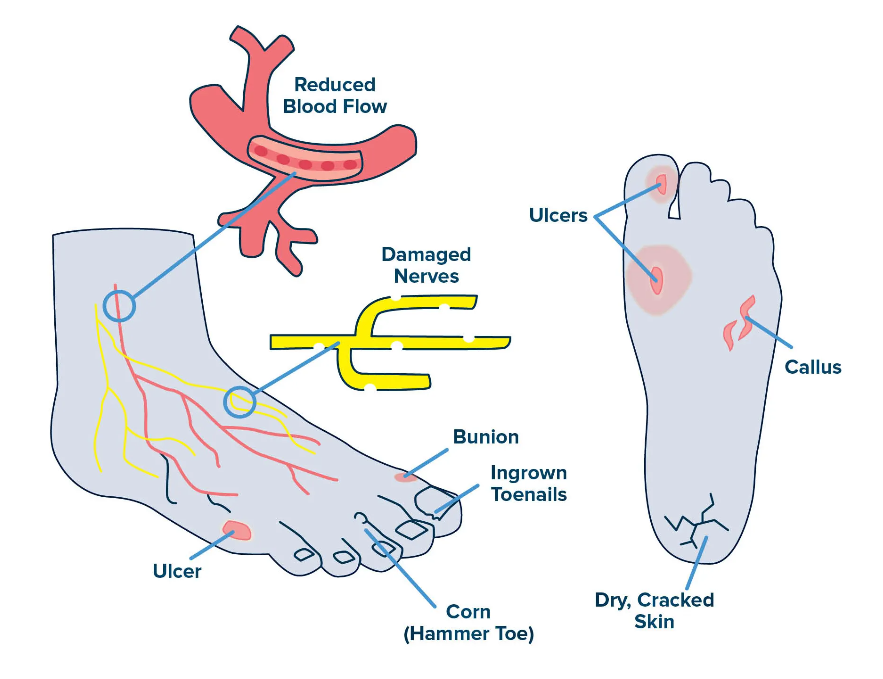
Ulcerations / Amputations
Patients with diabetes are likely to face dangerous foot problems.
Neuropathy and poor blood circulation are likely to lead to unrecognized irritation, injuries and ulcers that progressively develop into worse conditions.
Neuropathy ensures that injuries and pains are not felt, while poor circulation ensures that those injuries do not heal. This makes it likely for even a small cut, blister, or foot infection to develop into a much worse infection that can lead to amputation or even the loss of life if entirely ignored.
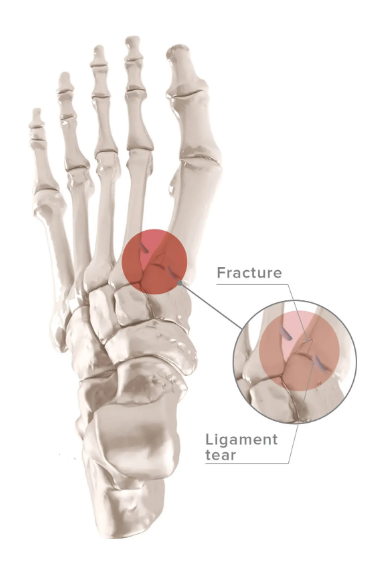
Factures
Metatarsal bones or large shaft bones of the forefoot meet with the cuneiforms and cuboid or bones of the midfoot. Fractures can result in dislocation, ligament damage, a may result in poor alignment during the process of healing if we are unable to properly position the foot.
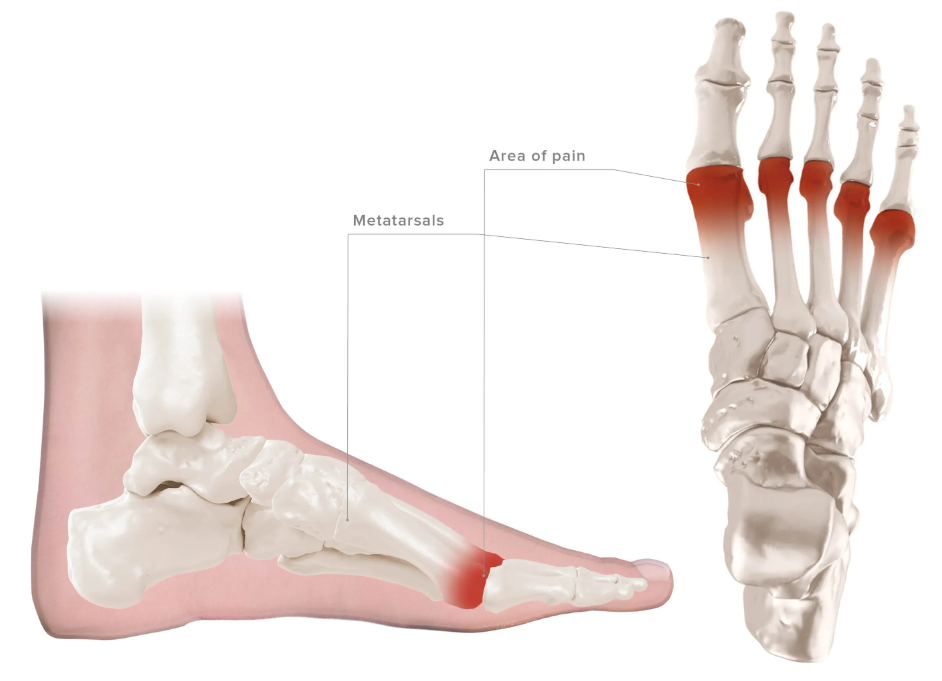
Metatarsalgia
Metatarsalgia is a broad diagnosis for a condition that describes pain around the head of the metatarsals, metatarsophalangeal joints and neighboring soft-tissue. Forces from physical activity applied on the forefoot can cause metatarsalgia. Most cases, around 90%, of metatarsalgia are biomechanically driven.
Frequently asked questions
Click to Learn More
Yes, an Orthotic can position our foot in the correct position so there is less stress on the structures (joints, ligaments, muscles) that are above our feet.
An evaluation of current limitations, pain, and presentation of the foot while standing and walking are needed to determine the underlying cause of our foot condition.
Modifications to our orthotics for pain relief go hand in hand with creating a custom fit orthotic device, we want to first find the underlying causation of the main problem while taking into consideration any other structual deviations in the bones of our foot.
There is always going to be a significant variation between each person’s foot, during an evaluation we are able to find possible problems within your feet and will discuss possible solutions to alleviate pain.
It is very common that many paitents will feel immediate pain relief from their custom orthotics, however we are placing our foot in the most ideal position for proper alignment. Therefore our feet must adjust to this new foot position which falls within the normal break-in time.
References: https://www.cedars-sinai.org/, https://www.kevinrootmedical.com/
